…Tejido de urdimbre complementaria, bordado en puntada de tallo sobre algodón y flecadura por torsión (borlas), fibra de camélido. El motivo central de esta bolsa es un personaje antropomorfo…
The petroglyphs of Kalina
Eight kilometers south of Alero de Taira is the archeological site of Calina Oeste, an open-air campcontaining the remains of several circular stone-walled dwellings. The camp’s former…
Social Organization Depicted on a Gourd
…trajes en forma de escudo y otros cinco llevan lo que parecen ser corazas de cuero, uno de los cuales sostiene un hacha en la mano. El personaje restante combina…
Historia
…In many ways, the Las Ánimas groups broke with the past to begin a new cultural tradition. The formerly common tembetás or lip adornments of the El Molle culture…
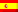
Paño: inkuña
…en la iconografía religiosa de las culturas contemporáneas del altiplano peruano-boliviano, como Pucara y Chiripa. Comparte con los tejidos tempranos andinos, el rasgo técnico de encadenar las orillas finales de…
History
…included communities as far away as the Atacama Desert, where similar ceremonial practices were already in use. In fact, these two peoples shared a common ritual language that enabled the…
Marine hunter-gatherers
At almost the same time that the terrestrial hunter-gatherer way of life emerged inland, along Chile’s extensive coastline other groups relied on the coastal environment as their…
Beliefs and Funerary Practices
…valleys that is a guardian spirit of animals and appears as a large guanaco that lives in the mountains. The practices and oral tradition of the Diaguita community of Chalinga,…
Aymara
…member plays a flute (sikuri or zampoña) and a drum at the same time. Sikuri bands participate in the patron saint festivals using a complex, typically Andean musical dialogue. The…
Economía
…by irrigation canals to complement the wild fruit they gathered from the algarrobo and chañar trees. They traveled frequently from East to West, seeking out products for trade—fish and mollusks…
Beliefs and funeral rites
Early Tiwanaku religious practices display influences from the Amazon basin, especially in its emphasis on shamanism associated with the consumption of hallucinogens. Later, official State rituals gradually led…
Horticulturalist of the Semi-arid north
By all indications, both ceramic making and horticulture seem to have been imported to the semi-arid North as innovations from outside the region; regardless of their provenance,…
Agriculturalists of the semi-arid north
…agricultural focus would cause the Diaguita and Copiapóto adopt a completely sedentary way of life, with most groups living in villages located near their farm fields. One such Diaguita settlement…
Agricultural-pastoralists absorbed by the inca state
Beginning in 1400 A.D., the societies inhabiting virtually all of the territory in the northern half of Chile, whether agricultural-pastoralist or nomadic hunter-gatherer, faced a dramatic change in…
Agricultural-pastoralists related toTiwanaku State
Around 600 A.D., the highlands and northernmost valleys of the Arid North would capture the economic interest of Tiwanaku, one of the first states to develop in…
Economía
…groups seem to have moved around locally according to seasonal cycles, with some longer journeys linking them with the coastal and trans-Andean regions. The other groups lived in communities that…
Art
Through their contact with the agricultural and herding groups living in the desert and inland valleys, these hunter-gatherer-fishers obtained objects such as ceramics, metal and fine woven cloth…
Art
…of five hundred years, they erected close to three hundred altars, called ahus, and carved more than six hundred stone moaistatues. These monumental pieces expressed the competition for power among…
Economy
…In ancient times, the people of Rapa Nui subsisted by growing several varieties of plantain, squash, tubers and sugar cane, and complemented their diet with fishing, hunting and gatheringfood…
Settlement pattern
As seafaring nomads, the Chonos moved around from island to island without having a home base. They spent most of their lives on board their dalcas, moving the…
Social organization
…family; but the women of the tribe governed their own activities and enjoyed equal rights. With no hierarchies, the community had no leader or chief; rather, the entire tribe was…
Economy
…The three distinct environments in which the groups of the Arica culture settled—mountain, valley and coast—allowed them access to complementary resources from different ecological strata. Surplus goods were moved…
Beliefs and funeral rites
…more complex ideology. The use of hallucinogenic powders inhaled through the nose (using tablets and tubes) appears to have become more prevalent as a ritual practice at this time, and…
History
…and perfected their ancestral way of life. The increasing complexity of the societies of the Atacameña area, which was closely tied to the traffic of goods with llama caravans, strongly…